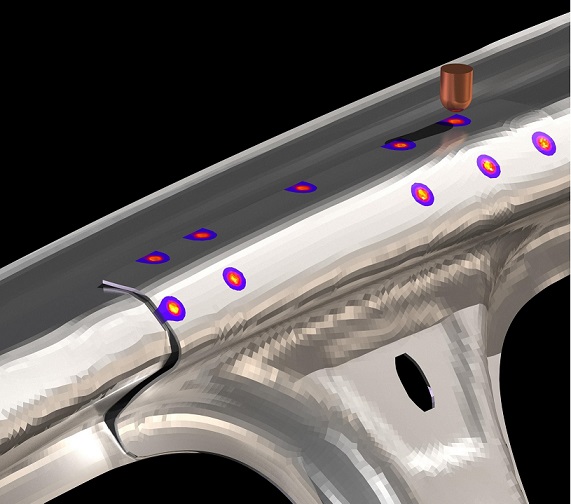
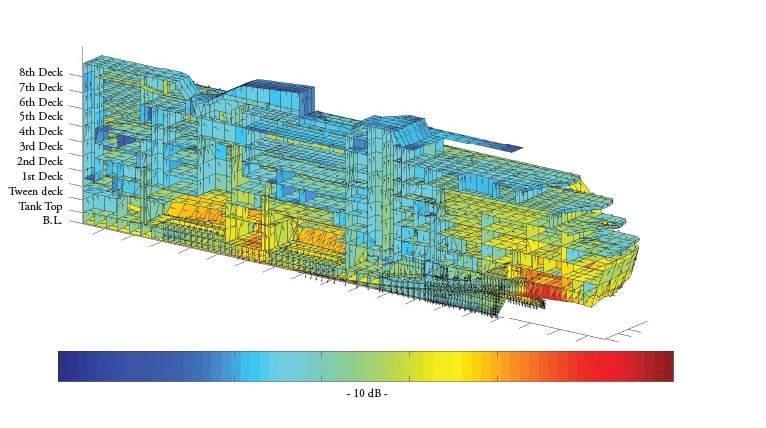
Stress relieving is a heat treatment process that is commonly used after welding to reduce residual stresses in the assembly. The process involves heating the metal to a specific temperature and holding it there for a certain amount of time, followed by controlled cooling.
The Stress Relief Heat Treatment process includes the definition of time-temperature curves for the heating, holding, and cooling phases. The curves are designed to ensure that the metal is heated and cooled at a rate that will reduce residual stresses without causing any additional distortion or cracking.
FEA Stress relief simulation is conducted taking into account two mechanisms: Stress relaxation due to decreased yield stress of the material during heating and time-dependent creep properties of the material. The simulation calculates the temperature distribution, thermal gradients, and residual stresses in the welded assembly after the stress relieving heat treatment process.
The main goal of stress relieving is to improve the overall structural integrity of the assembly. Residual stresses can cause distortion, warping, and cracking in the metal, leading to premature failure. By reducing these stresses through stress relieving, the assembly can perform more reliably and have a longer service life.